
NIFT Coaching in Bangalore: A Complete Roadmap from Beginner to Admit
Preparing for the NIFT entrance exam can be both exciting and challenging. With the right direction, structured learning, and consistent practice, success becomes achievable. This

Music is the art of creating a composition by organizing sounds in time using the elements of melody, harmony, rhythm, and timbre. It is a cultural characteristic of all human communities that is universal. Pitch (which determines melody and harmony), rhythm (and its linked notions tempo, meter, and articulation), dynamics (loudness and softness), and the auditory qualities of timbre and texture are all prevalent features in general definitions of music (which are sometimes termed the “color” of a musical sound). Some of these aspects may be emphasized, de-emphasized, or omitted depending on the style or type of music. There are solely instrumental pieces, solely vocal pieces (such as songs without instrumental accompaniment), and pieces that combine singing and instruments; there are solely instrumental pieces, solely vocal pieces (such as songs without instrumental accompaniment), and pieces that combine singing and instruments.
 The creation of works of music (songs, melodies, symphonies, and so on), music criticism, music history studies, and aesthetic assessment of music are all activities that describe music as an art form or cultural activity in the broadest sense. Melodies are tones organized horizontally, whereas harmonies are tones ordered vertically, according to ancient Greek and Indian philosophers. “The harmony of the spheres” and “it is music to my ears” are common phrases that imply that music is often well-ordered and enjoyable to listen to.
The creation of works of music (songs, melodies, symphonies, and so on), music criticism, music history studies, and aesthetic assessment of music are all activities that describe music as an art form or cultural activity in the broadest sense. Melodies are tones organized horizontally, whereas harmonies are tones ordered vertically, according to ancient Greek and Indian philosophers. “The harmony of the spheres” and “it is music to my ears” are common phrases that imply that music is often well-ordered and enjoyable to listen to.
Music’s origin, performance, meaning, and even definition are all influenced by culture and social context. Indeed, several new forms or styles of music have been attacked as “not being music” throughout history. Popular music, traditional music, art music, music composed for religious rituals, and work songs such as chanteys are all examples of different forms of music. From carefully ordered compositions like Classical music symphonies from the 1700s and 1800s to spontaneously played improvisational music like jazz and avant-garde types of chance-based current music from the 20th and 21st centuries, the music spans the spectrum.
Individuals who write new songs and musical pieces (songwriters and composers), individuals who perform music (including orchestra, jazz band, and rock band musicians, singers, and conductors), individuals who record music (music producers and sound engineers), individuals who organize concert tours, and individuals who sell recordings, sheet music, and symphonies are all part of the music industry. Music critics, music journalists, and music academics can review and evaluate a piece and its performance even after it has been played.

There are several health benefits attached to making music as one of your hobbies. Even infants as young as a year old can benefit from music exposure because it improves their communication skills, resulting in more frequent smiles and indicators of sophisticated brain responses.
Below mentioned are some of the benefits:

Preparing for the NIFT entrance exam can be both exciting and challenging. With the right direction, structured learning, and consistent practice, success becomes achievable. This

Preparing for the architecture entrance exam requires the right strategy, structured learning, and expert mentoring. With increasing competition, NATA coaching has become essential for students

By signing up for IgniteIndia. You agree to the Terms of Services and PrivacyPolicy of the platform.
Fashion & Textile Designer, Educational and Career Counselor. He is an alumnus of NIFT and won the Best Graduation Project Award. He is guiding students from the past 10 years.
Ignite India Education is inspired by the former President of India Bharat Ratna Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam’s vision of “India Beyond 2020”. Our aim is to fulfil his vision by empowering society and transforming India into a developed nation through education.
Fashion & Textile Designer, Educational and Career Counselor. He is an alumnus of NIFT and won the Best Graduation Project Award. He is guiding students from the past 10 years.
Ignite India Education is inspired by the former President of India Bharat Ratna Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam’s vision of “India Beyond 2020”. Our aim is to fulfil his vision by empowering society and transforming India into a developed nation through education.
Fashion & Textile Designer, Educational and Career Counselor. He is an alumnus of NIFT and won the Best Graduation Project Award. He is guiding students from the past 10 years.
Ignite India Education is inspired by the former President of India Bharat Ratna Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam’s vision of “India Beyond 2020”. Our aim is to fulfil his vision by empowering society and transforming India into a developed nation through education.
Fashion & Textile Designer, Educational and Career Counselor. He is an alumnus of NIFT and won the Best Graduation Project Award. He is guiding students from the past 10 years.
12 Years of Experience
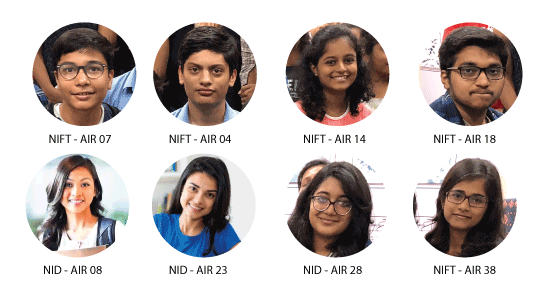






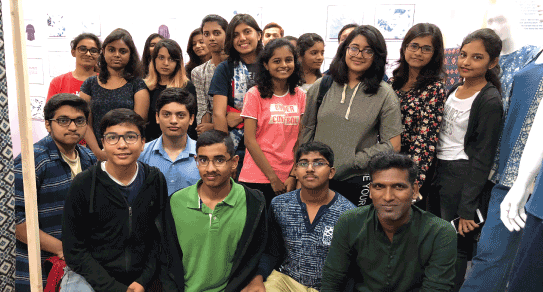
Ignite India Alumni networks provide the long-term value to an educational institution by giving alumni the chance to stay in contact and continue to learn from each other long after they have left Institute. Ignite India is a Well Known Design Institute that equips students for success in career.